Search the documentation
- Simple text search: If you don't use quotation marks before and after the search word or phrase, the search performs "simple text" search where the search results contain a ranked list of the topics that contain all of the words in the Search field, but not necessarily in the exact order or together.
- Exact phrase search: If you use quotation marks before and after the search word or phrase (like "search features", the search performs an "exact match "search where the search results contain a ranked list of the topics that only contain an exact match of words or phrase is in the Search field (excluding the quotation marks).
Search features
- Case‑insensitive Matches: The search is not case‑sensitive. For example, a search for the word
runwill find matches forRunandrunand RUN. - Matches with Variant Endings: The search includes matches with variant ending. For example, a search for the word
runwill also find matches for words such as,runner,running, andruns. Because matches are not case‑sensitive, the results will include topics containing matches such as,Runner,Running, andRuns. - Exact phrase search: You can search for exact phrases by enclosing their search terms in quotation marks. This is useful when end users want to restrict a search to locate terms that appear in an exact order. For example, you might want to search for a phrase such as
"the page settings window”. - Partial‑word searches: The search includes partial‑words. This search method is similar to simple text search, only it allows searches for partial‑word and number strings.
- Powerful Boolean searches: You may use Boolean operators in your search to focus your search results. For more information, see Boolean searches.
- Synonyms: We have identified some words as synonyms in the documentation system and the search results include all the topics that include the either the word or it’s defined synonyms.
For example:
- Entering
create,add, ornewproduces the same search results. - Entering
removeordeleteproduces the same search results. - Entering
open,display, orappearproduces the same search results. - Entering
edit,change, ormodifyproduces the same search results. - Entering
jurisdiction,county,parish,recipient,township, orborough produces the same search results.
- Entering
Boolean searches
Boolean operators can be used in combination with search terms to increase or decrease the number of search results.
Our documentation supports Boolean operators such as AND, OR, NEAR, NOT, and ( ). The Boolean operators are not case sensitive.
Here is a list of the Boolean operators that work in the search, as well as some examples and notes.
| Description | Variable | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Search for one or more words. When a group of words are entered into the search field, "or" is inferred. |
|
|
|
Search for a phrase. Note: The search engine ignores certain commonly used words. For example, a, an, the, of, to, be, you, your, when, however, for, that, can (and more). If your search results are not successful, trim out some of the less important words. |
" " (wrap a text string in quotes) |
|
|
Search for "either of" or "any of" specific strings. |
OR (case insensitive) | (pipe symbol) |
|
|
Search for two or more specific strings. |
AND (case insensitive) + (plus symbol) & (ampersand) |
cat AND dog "windy day"+rain "noodle soup"&"animal crackers" |
|
Search for all topics that do not contain something. |
NOT (case insensitive) ! (exclamation mark) |
not fish ! flood |
|
Search for all topics that contain one string and do not contain another. |
^ (carat symbol) |
cat ^ mouse |
|
Combinations of the above. |
( ) parenthesis |
cat and (dog or mouse) cat or dog (! fish) |
Wildcard searches
The search function does not support the use of the asterisk "*" or question mark "?" as wildcard characters in search strings. However, the search function returns close search results to the search term including plural, future, and past tense versions of the search terms. See Close Words.
Narrow the search using “AND”, “ and ”, “+”, “&” or a “blank space”
Entering “ AND ”, “ and ”, “+”, “&” or a “blank space” performs the same operation and retrieves all topics that contain all of the search terms it separates. The “ and “ operator is not case sensitive.
- Type a blank space between the words (in the place of “AND”). The “ AND ” is always inferred.
- Type “ AND ” with a space before and after between two or more terms.
- Type the plus symbol (+) without spaces before and after in the place of “ AND ”.
- Type the ampersand symbol (&) without spaces before and after in the place of “ AND ”.
Example: To find the topics that included all of the terms submitter, recipient, and agent, enter any of the following:
- submitter recipient
- submitter AND recipient
- submitter and recipient
- submitter+recipient
- submitter&recipient
Broaden the search using “ OR ”, “ or ”, or pipe symbol “|”
Entering “ OR ” or the pipe symbol “|” between two or more terms broadens the search and retrieves all topics that contain any of the search terms it separates. The “ OR “ operator is not case sensitive.
Example: To find the topics that included any of the terms submitter, recipient, or agent, enter any of the following:
- submitter OR recipient OR agent
- submitter Or recipient Or agent
- submitter or recipient or agent
- submitter|recipient|agent
Limit the search using “ NOT ”, “ not ”, an exclamation point (!) or a carat symbol (^)
Entering “ NOT ”, “ not ”, the carat symbol (^) or the exclamation mark (!) between terms finds the topics that contain the first term but not the second term. These can be used interchangeably and “ NOT ” is not case sensitive.
Example: To find the topics that include the first term but not the second term, enter any of the following:
- submitter NOT recipient
- submitter not recipient
- submitter^recipient
- submitter!recipient
Use parentheses to combine Boolean phrases and search terms
Enter parentheses ( ) around the combined terms.
Example: To search for topics containing agent and either the term recipient or submitter, search for:
- agent AND (recipient OR submitter)
- agent and (recipient or submitter)
- agent (recipient|submitter)
- agent (recipient or submitter)
- agent&(recipient|submitter)
- agent+(recipient OR submitter)
Boolean searches
Boolean operators can be used in combination with search terms to increase or decrease the number of search results.
Our documentation supports Boolean operators such as AND, OR, NEAR, NOT, and ( ). The Boolean operators are not case sensitive.
Here is a list of the Boolean operators that work in the search, as well as some examples and notes.
| Description | Variable | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Search for one or more words. When a group of words are entered into the search field, "or" is inferred. |
|
|
|
Search for a phrase. Note: The search engine ignores certain commonly used words. For example, a, an, the, of, to, be, you, your, when, however, for, that, can (and more). If your search results are not successful, trim out some of the less important words. |
" " (wrap a text string in quotes) |
|
|
Search for "either of" or "any of" specific strings. |
OR (case insensitive) | (pipe symbol) |
|
|
Search for two or more specific strings. |
AND (case insensitive) + (plus symbol) & (ampersand) |
cat AND dog "windy day"+rain "noodle soup"&"animal crackers" |
|
Search for all topics that do not contain something. |
NOT (case insensitive) ! (exclamation mark) |
not fish ! flood |
|
Search for all topics that contain one string and do not contain another. |
^ (carat symbol) |
cat ^ mouse |
|
Combinations of the above. |
( ) parenthesis |
cat and (dog or mouse) cat or dog (! fish) |
Narrow the search using “AND”, “ and ”, “+”, “&” or a “blank space”
Entering “ AND ”, “ and ”, “+”, “&” or a “blank space” performs the same operation and retrieves all topics that contain all of the search terms it separates. The “ and “ operator is not case sensitive.
- Type a blank space between the words (in the place of “AND”). The “ AND ” is always inferred.
- Type “ AND ” with a space before and after between two or more terms.
- Type the plus symbol (+) without spaces before and after in the place of “ AND ”.
- Type the ampersand symbol (&) without spaces before and after in the place of “ AND ”.
Example: To find the topics that included all of the terms submitter, recipient, and agent, enter any of the following:
- submitter recipient
- submitterAND recipient
- submitter and recipient
- submitter+recipient
- submitter&recipient
Broaden the search using “ OR ”, “ or ”, or pipe symbol “|”
Entering “ OR ” or the pipe symbol “|” between two or more terms broadens the search and retrieves all topics that contain any of the search terms it separates. The “ OR “ operator is not case sensitive.
Example: To find the topics that included any of the termssubmitter, recipient, or agent, enter any of the following:
- submitter OR recipient OR agent
- submitter Or recipient Or agent
- submitter or recipient or agent
- submitter|recipient|agent
Limit the search using “ NOT ”, “ not ”, an exclamation point (!) or a carat symbol (^)
Entering “ NOT ”, “ not ”, the carat symbol (^) or the exclamation mark (!) between terms finds the topics that contain the first term but not the second term. These can be used interchangeably and “ NOT ” is not case sensitive.
Example: To find the topics that include the first term but not the second term, enter any of the following:
- submitter NOT recipient
- submitter not recipient
- submitter^recipient
- submitter!recipient
Use parentheses to combine Boolean phrases and search terms
Enter parentheses ( ) around the combined terms.
Example: To search for topics containing agent and either the term recipient or submitter, search for:
- agent AND (recipient OR submitter)
- agent and (recipient or submitter)
- agent (recipient|submitter)
- agent (recipient or submitter)
- agent&(recipient|submitter)
- agent+(recipient OR submitter)
Understand search results
When the Search (![]() ) button in the search bar is pressed, the search is initiated and the results are displayed in the right panel.
) button in the search bar is pressed, the search is initiated and the results are displayed in the right panel.
The search results indicate how many topics were returned that meet the search criteria and lists the topics with their links in order of relevance (from most to least relevant) based on the precision and frequency of the search term or terms.
Case insensitive and tense variations
The search results are case insensitive (all search results in upper case, lower case, and mixed case formats) and returns plural or singular variations and future tense and past tense variations of the search terms.
Close words
The search returns close occurrences of the term including, but not limited to, the plural form, past tense form, and future-tense form. Searching either "migrate" or "Migrate" each return variations of the search term such as "Migrate", "migrate","Migration", "migration", "Migrated", "migrated", "Migrations", and "migrations" with both capitalized and non-capitalized versions.
Search result highlighting
When you select a link for one of the topic from the search results, the topic is opened in the right panel.
The search terms are highlighted as follows:
- The first search term is highlighted in yellow .
- The second search term is highlighted in light blue .
- The third search term is highlighted in light green .
- The fourth search term is highlighted in dusty rose .
- The fifth search term is highlighted in light purple .
- The sixth search term is highlighted in brown with white characters .
- The seventh search term is highlighted in green with white characters .
- The eighth search term is highlighted in olive with white characters .
- The ninth search term is highlighted in blue with white characters .
- The tenth search term is highlighted in purple with white characters.
Example:
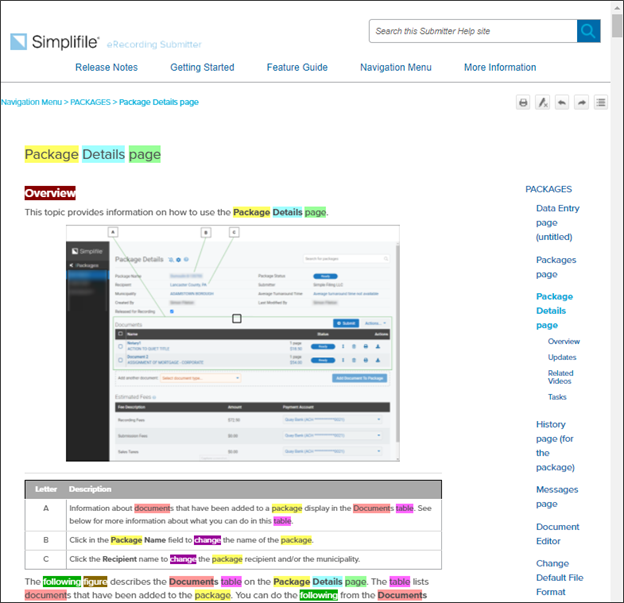
If you enter the search package details page document table overview following figure describes change, the search results page finds one topic, the Package Details page. When you select the link in the search results list, you will see something similar to the following:
Searching the documentation
- Open the document. See How to open the documentation.
- Go to the search toolbar near the top right corner of the page.
- In the Search field enter the search words or phrase you want to find.
- Optional: Select the search type. Select the middle dropdown list button to select the search type.
- Select the Search
 button in the search toolbar to start the search.
button in the search toolbar to start the search.The search results, ranked by relevance with a sentence or two from each topic.
- Select the wanted topic link in the search results page.
The selected topic opens with exact search words highlighted to help you quickly find the information for which you searched. Non‑exact matches (like variant endings) are not highlighted.