adjustable rate mortgage (ARM) [also called variable rate mortgage (VRM)]
A mortgage whose interest rate over the life of the loan may change from the original rate. Rates may go up or down and are usually tied to an economic indicator and a time period. Some ARMS can convert to a fixed interest rate after a period of time.
adjustment
A change in a pro‑ration that occurs if the closing date of a mortgage occurs before regular payments begin. For example, if the mortgage closes on the 18th and mortgage payments begin on the first of the following month, prorations must be adjusted to indicate that the buyer owned the property for twelve additional days.
affidavit
An affidavit of title is a legal document provided by the seller of a piece of property that explicitly states the status of potential legal issues involving the property or the seller. The affidavit is a sworn statement of fact that specifies the seller of a property holds the title to it.
agent / real estate agent
A person authorized to act on anothers behalf. In real estate, this agent may be a listing agent who represents the seller, a selling agent who represents the buyer, or a dual agent who represents both the seller and the buyer. A transaction agent or broker represents neither party but helps the transaction to be completed. An agent must work for a licensed real estate broker, who can function as an agent but who also can have other agents working as employees.
In Simplifile, a closing agent or settlement agent is the party that submits documents to recording jurisdictions to be legally recorded.
amortization
The repayment of a loan over time. With each payment, the principal (the original amount borrowed) is reduced. An amortization schedule shows each payment amount, how much of each payment is applied to the principal, how much is applied to the interest, and how much remains to be paid. Negative amortization occurs when loan payments do not cover the interest due. The unpaid amount is added to the principal. Since the principal increases instead of decreasing, the amortization is negative instead of positive.
assignment of leases and rents
Sometimes called Assignment of Leases, Rents and Profits or simply Assignment of Rents, this is a document attached to a mortgage loan agreement which entitles the lender to any income (from leases, rents, etc.) derived from the property once the owner defaults on the loan.
Automated Clearing House (ACH)
An automated clearing house (ACH), or automated clearinghouse, is an electronic network for financial transactions, generally domestic low value payments. An ACH is a computer‑based clearing house and settlement facility established to process the exchange of electronic transactions between participating financial institutions. It is a form of clearing house that is specifically for payments and may support both credit transfers and direct debits.
ACHs are designed for high‑volume, low‑value payments, and charge fees low enough to encourage the transfer of low‑value payments. The system is designed to accept payment batches, so that large numbers of payments can be made at once.
bargain and sale deed
Bargain‑and‑Sale deed is usually used to convey property to a buyer for valuable consideration. Bargain and sale deed carries, contains no warranties against liens or other encumbrances against title, except any that the grantor specifically sets out in the deed. It is implied that the grantor has the right to transfer the deed. It is also sometimes referred to as a special or limited warranty deed.
Be as “e” as You Can Be
a prescribed strategy for implementing e closing best practices based on package types. In addition, the strategy needs to be comprehensive, moving quickly from pilots to all package types to drive change. E Closing package types are classified based on the degree of accepted and allowable electronic signatures. Closing packages included in a lender’s strategy are:
- Ink‑Signed ‑ No documents can be e‑Signed.
- Hybrid ‑ Ancillary documents are e‑Signed.
- Hybrid & eNote ‑ Ancillary documents and notes are e‑Signed.
- Fully Digital ‑ Security and notary documents are e‑Signed/e‑Notarized. Ancillary documents are e‑Signed.
button
In the Simplifile application, a “button” may be one of several things.
A button may be a graphical element with a distinct border that initiates an action. For example, the Save
button.
A button often (but not always) includes button name inside the button border and may or may not contain a symbol (or icon) inside the border.
In the documentation, this type of button is most often represented with its name in initial capital letter and bold. The word “button” may or may not be included in the text. For example, “Select the Save
button”.
A text button may be blue text with or without an icon that initiates an action. For example, the
button.
In the documentation, this type of button is most often represented with its name in blue and often without the icon. For example, “Select the Register More Counties button.” The word “button” may or may not be included in the text. For example, “Select the Register More Counties button”.
An icon button may be only an icon that initiates an action. For example the Edit
button. Some icons are just visual indicators and do not initiate an action.
In the documentation, when icons are used as buttons we usually include the function or name of the button in bold and the icon. For example, Select the Edit
button, the Menu
(ellipsis) button, and the Add
button. Icon buttons may or may not be inside a border in the documentation.
Buttons and icon buttons differ from links in that links are often colored and underlined text and usually open web pages where buttons and icon buttons usually open pages, windows, or tools within the Simplifile application from which you may do an activity or activities. The blue underlined cross‑reference topic links in this Simplifile documentation are links.
Not all icons are buttons. Some icons are visual indicators or status or other properties that do not initiate an action.
chain of lien
A legal document issued when someone files a claim against real property for money or services owed. For example, a roofer who has not been paid might file a claim of lien against the property where the new roof was installed. The owner cannot sell the property until the lien is paid off to clear the title to the property.
chain of title
A recorded history of all ownership documents for a particular piece of property. A chain of title is the sequence of historical transfers of title to a property. It is a valuable tool to identify and document past owners of a property and serves as a property's historical ownership timeline. The "chain" runs from the present owner back to the original owner of the property.
claim of lien
A legal document issued when someone files a claim against real property for money or services owed. For example, a roofer who has not been paid might file a claim of lien against the property where the new roof was installed. The owner cannot sell the property until the lien is paid off to clear the title to the property.
closing (also called escrow closing, real estate closing, settlement)
In real estate, the process that occurs when all parties involved in the purchase or refinance of real property execute legally binding documents that pass the real property title from seller to buyer, and the seller is paid.
A closing agent or settlement agent organizes and supervises a closing.
closing costs (also called settlement fees)
The expenses incurred when a property is purchased or refinanced. They may include but are not limited to attorney’s fees, points, credit report fees, document preparation fees, mortgage insurance premiums, inspections, surveys, appraisals, property taxes, deed recording fees, and homeowners insurance.
closing disclosure (CD) (also called disclosure)
Contains details about a loan such as the fees and other closing costs required to finalize the loan, the terms of the loan, and projected monthly payments. As of 2015, this single document replaces the HUD‑1 settlement statement and the Truth in Lending Disclosure document for most housing loans secured by real estate.
closing statement (also called settlement or settlement sheet)
In real estate, the final statement of credits and expenses as approved during closing. The closing statement lists the source of funds and the distribution of funds in connection with the purchase and/or mortgaging of residential property.
conventional loan / conventional mortgage
A real estate loan that is neither insured by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) nor guaranteed by the Veterans Administration. Conventional loans are subject to the terms of their particular organization. Because the lender is not required to follow federal guidelines, the conditions of the loan may be more flexible.
convertible ARM
An adjustable rate mortgage (ARM) [also called variable rate mortgage (VRM)] that can be changed into a fixed‑rate mortgage during a specified period and under certain conditions.
credit report
An official summary of someone’s financial history prepared by a credit‑reporting agency or bureau, including the current status of the person’s credit standing. Lenders use these reports to help determine a loan applicant’s creditworthiness. The credit report fee is paid to a lender so that the lender can obtain a loan applicant’s credit history directly from the credit‑reporting agency or bureau.
county
In Simplifile, a recording county (or jurisdiction or recipient) receives documents for recording. Counties (or jurisdictions) are integrated into Simplifile in the following primary ways:
- Quick Start jurisdictions log directly into Simplifile and record documents through the Simplifile application. After recording, the documents are maintained in our system but the county can print or save a copy for their records.
- Quick Start Plus jurisdictions log in and record documents through the Simplifile application, but after recording an upload queue in Simplifile lets the county (or jurisdiction) transfer recorded documents to a land records system. Land record systems provide long‑term storage of eRecordings and are typically connected with the county’s website.
- Vendor / 3rd Party jurisdictions maintain a separate software system (such as Property Info, Brown Tech, or Harris Recording) where Simplifile imports data entered by submitters into Simplifile. Each package receives a tracking number (RID) that both Simplifile and the vendor system use to track the package. The vendor system records and maintains the documents.
debt‑to‑income ratio (also called back‑end ratio)
Used with the mortgage‑to‑income ratio (or front‑end ratio) to determine how much of a mortgage someone can afford. The debt‑to‑income ratio adds the potential housing expense to any other consumer debt and divides the total by the borrower’s gross monthly income. It typically has a maximum limit of 35%.
deed (also called transfer document)
A legal document that transfers ownership or title to a property from one person or entity to another. Each type of deed (for example, a disclaimer deed, grant deed, warranty deed, fee simple deed, transfer deed, or quitclaim deed) has some legal differences but they all convey property ownership. Sellers and buyers sign the deed during closing. It is then recorded.
deed of trust
A document that transfers legal title to a trustee, who holds the title as security for a loan between a borrower (trustor) and lender (trust deed beneficiary). Trust deeds always involve at least three parties. The trustee’s main function is to sell the property at public auction if the borrower defaults on the loan payments. Compare with mortgage.
The following states typically use trust deeds.
|
Alabama |
Alaska |
Arizona |
Arkansas |
|
California |
Colorado |
District of Colombia |
Georgia |
|
Idaho |
Maryland |
Massachusetts |
Minnesota |
|
Mississippi |
Missouri |
Montana |
Nebraska |
|
Nevada |
New Hampshire |
New Mexico2 |
North Carolina |
|
Oklahoma1 |
Oregon |
Rhode Island |
South Dakota |
|
Tennessee |
Texas |
Utah |
Vermont |
|
Virginia |
Washington |
West Virginia |
|
1 Unless homeowner requests judicial
2 Sometimes
dialog, dialog box
See window.
disclosure
See Simplifile Glossary.
Doc Viewer
A short name for the Document Editor and Document Viewer.
Document Editor
The Submitter, Document Builder, and Settlement Agent version of the Simplifile Document Editor/Viewer tool. The Recipient component and Lender component version of the tool is called the Document Viewer. Both the Document Viewer and Document Editor use and access the same technology and documents, but the Document Editor is configured for submitters, Document Builder users, and settlement agents.
Document Viewer
The Recipient component and Lender component version of the Simplifile Document Editor/Viewer tool. The Submitter, Document Builder, and Settlement Agent version of the tool is called the Document Editor. Both the Document Viewer and Document Editor use and access the same technology and documents, but the Document Viewer is configured for counties (or jurisdictions) and lenders.
earnest money (also called deposit)
A sum of money offered in good faith by a prospective purchaser at the time of the purchase offer. These funds are typically deposited into an escrow account and held until the real estate closing takes place. At the closing, the buyer is either given credit for the earnest money that has already been paid, or it is returned to the buyer. These funds may also be returned to the buyer if the sale fails.
easement
The right to use another person's property for a specific, limited purpose. For example, utility companies may have easements over property so they can work with power or sewer lines and so forth. Closing documents and land surveys should indicate easements, which must be acceptable to the mortgage company.
equity (also called real property value)
The difference between the current fair market value of a property and the amount still owed on the mortgage, lowered by liens, second mortgages, and other additional debts against the property. The amount an owner would receive from the sale of the property.
equity loan
An equity loan lets you draw on the real property value of your real estate. The fair market value of the property minus any current mortgages or other debts secured by the property help determine the amount of the loan. See also home equity line of credit (HELOC).
escrow
Something of value (such as a deed, a bond, money, or property) held by a neutral third party until a specified obligation or condition has been met. For example, someone’s monthly mortgage payment may include funds to pay for future taxes and insurance in addition to the principal and interest. This escrow is held by the lender until taxes and insurance are due; then the mortgage company pays the taxes and insurance on the borrower’s behalf.
estimated fees
Simplifile's fee estimates are based on schedules provided by the associated recording county (or jurisdiction) and are calculated on package properties known to us at the time of submission. Such properties may include but not be limited to:
- page counts
- document types
- indexing data such as party count and consideration amount
However, additional factors may affect final recording fees that cannot be automatically detected by Simplifile, and therefore are not included in our estimates.
Simplifile does not guarantee the accuracy of our fee estimates, and submitters are responsible for all recording fees and taxes assessed by the recording county (or jurisdiction). Most jurisdictions post comprehensive fee schedules on their websites, and users are encouraged to consult these sites if additional certainty regarding fees and taxes is required.
Fair Credit Reporting Act
A federal law that protects consumers by regulating the consumer credit agencies’ disclosure of individuals’ credit histories. The Act also establishes guidelines and procedures for correcting errors disclosure of individuals’ credit histories. The Act also establishes guidelines and procedures for correcting errors on errors on your credit report.
Federal National Mortgage Association (Fannie Mae)
A federal agency established in 1938 to purchase mortgage loans from lenders as an investor. Fannie Mae originally bought FHA loans, but now invests in conventional, FHA, and VA loans. Fannie Mae’s Community Home Buying Program helps low‑to‑moderate income families buy a home by decreasing the amount of down payment required and allowing higher debt‑to‑housing ratios in some cases.
Federal Housing Administration (FHA)
An agency of the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) meant to encourage improvement in housing standards, to provide insurance for mortgages, and to help stabilize the mortgage market. FHA’s main activity is to insure residential mortgage loans made by banks and private lenders. The FHA sets standards for construction and underwriting but does not lend money or build housing. See also entries beginning with FHA.
filter
In the Simplifile application, a “filter” is a set of parameters that must be met for the information to be displayed in a page or window. To help you quickly find the information and documents with which you work, you may create filters in many of the pages. Often a filter is represented by a Funnel
button. Selecting the Filter button opens a filter window from which you can choose your filter parameters.
flood insurance
An insurance policy that covers property in a flood area against flood damage. When purchasing real estate, a survey is typically required where there is any risk of flooding to the property. A lender may require flood insurance before granting a loan on a property at risk for flooding.
Government‑Sponsored Enterprise (GSE)
A financial services company intended to make borrowing easier for certain sectors such as students, farmers, and home owners. See Fannie Mae and Federal National Mortgage Association (Fannie Mae).
hazard insurance
A borrower‑purchased insurance policy that covers a property against loss due to hazards such as fire, hailstorms, and other natural events. Some types (such as for flood or earthquake) must be purchased separately. Often a lender requires the borrower to pre‑pay part of the annual premium at closing. The monies are held for the borrower in an escrow account and paid by the lender when due.
home equity line of credit (HELOC)
Similar to an equity loan, but instead of a single large loan, this loan lets owners withdraw and repay funds on an as‑needed basis.
homeowners insurance
A borrower‑purchased insurance policy that covers a property against damage to the house itself or to personal property inside the home. This type of policy usually also covers accidents that may occur inside the home or on the property. Often the borrower pays the premiums to the lender monthly, along with the principal / interest payment. The monies are held for the borrower in an escrow account and paid by the lender when due. See also hazard insurance.
icon
In the Simplifile application, an “icon” is a small graphical element usually without a border.
An icon may (but is not required to) display with its name in light blue. For example,
.
Some icons are visual indicators of status or other properties that do not initiate an action.
When an icon initiates an action it is also considered button.
In the documentation, when icons are used as buttons we usually include the function of the icon button in bold, the icon in parentheses, and the word “icon” or "button" may or may not be included in the text. For example, “Select the Edit
button.”
in‑person electronic notarization (IPEN)
In‑person electronic notarization (IPEN) requires the signer and notary to be in the same location but allows them to apply electronic signatures to documents. Depending on the state, there are additional rules around IPEN. Some states require the technology vendor to register with the secretary of state and a separate registration may be required for the notary. Your notary vendor should be able to assist in fulfilling these requirements. Simplifile’s Document Builder fulfills these requirements for servicers in applicable jurisdictions. A newer and less‑widely accepted electronic notarization option which does not require the signer and notary to be in the same location and can typically be done via webcam.
interest rate
The amount charged to borrow money, expressed as a percentage of the loan’s principal. Unlike the annual percentage rate (APR), the interest rate does not include additional fees, finance charges, and closing costs related to the loan.
jurisdiction
In Simplifile, a recording county (or jurisdiction or recipient) receives documents for recording. Counties (or jurisdictions or recipients) are integrated into Simplifile in the following primary ways:
- Quick Start jurisdictions log directly into Simplifile and record documents through the Simplifile application. After recording, the documents are maintained in our system but the county can print or save a copy for their records.
- Quick Start Plus jurisdictions log in and record documents through the Simplifile application, but after recording an upload queue in Simplifile lets the county (or jurisdiction) transfer recorded documents to a land records system. Land record systems provide long‑term storage of eRecordings and are typically connected with the county’s website.
- Vendor / 3rd Party jurisdictions maintain a separate software system (such as Property Info, Brown Tech, or Harris Recording) where Simplifile imports data entered by submitters into Simplifile. Each package receives a tracking number (RID) that both Simplifile and the vendor system use to track the package. The vendor system records and maintains the documents.
legal description
In real estate, a document that uses information such as the land lot, the subdivision name, and the block or parcel to describe, locate, and identify a piece of property that is being bought or transferred in some other way. A binding real estate contract must include an accurate legal description.
listing (also called listing contract or listing agreement)
An agreement between a real estate broker or agent (called a listing agent, seller’s agent, or broker) and a seller. The agreement gives the broker the rights to advertise the property and represent the seller, often for a specified period of time. In most cases, the brokerage earns its commission only if the agent finds a viable buyer for the property within the time of the listing contract.
loan application
A request to borrow money that includes information about the borrower’s financial situation and the property being purchased. At minimum, it should include the borrower’s name, income, and Social Security number (or other unique identifier if the borrower has no Social Security number); the property address; an estimate of the value of the property; and the amount of the desired mortgage loan.
loan estimate
An informational document that contains estimated information about a requested loan such as the potential closing and ongoing costs and possible changes in the interest rate. As of 2015, this single document replaces the Good Faith Estimate (GFE) and an initial Truth in Lending Disclosure document for most housing loans secured by real estate.
loan origination
The process of creating a mortgage loan. During the process, the borrower provides financial information to the lender, who then determines the type, amount, and interest of loan the borrower can afford. The loan originator is the person or entity, usually a bank or mortgage broker, who takes a loan application and offers or negotiates the terms of the mortgage for financial gain.
loan‑to‑value (LTV)
A comparison of the amount of a mortgage and the value or sales price of the property being mortgaged. For a purchase, LTV divides the loan amount by the lower of the sales price of a home or the appraised value of the home. For a refinance, LTV divides the loan amount by the appraised value. The higher the LTV, the more risk for the lender, and the loan will likely cost the borrower more to offset the risk.
lock‑in / rate lock
An agreement where the lender guarantees a specific interest rate and loan terms for a certain amount of time at a particular cost. If interest rates go up, the borrower’s rate does not. If interest rates go down, the seller may let the borrower re‑lock at the lower rate (a float down option), but may also require more discount point fees.
LTV
See loan‑to‑value (LTV).
MISMO, (Mortgage Industry Standards Maintenance Organization)
MISMO® is the standards development body for the mortgage industry. MISMO developed a common language for exchanging information for the mortgage finance industry. MISMO standards are accepted and deployed by every type of entity involved in creating mortgages, and they are required by most regulators, housing agencies and the GSEs that participate in the industry.
mortgage
A real property lien that gives the lender the property as security if the borrower should default on the mortgage. With a mortgage, the mortgagor gives legal title directly to the mortgagee. A mortgage requires a judicial foreclosure. Compare with Simplifile Glossary.
The following states typically use mortgages.
| Connecticut | Delaware | Florida | Hawaii |
| Illinois | Indiana | Iowa | Kansas |
| Kentucky | Louisiana | Maine | Michigan |
| New Jersey | New Mexico3 | New York | North Dakota |
| Ohio | Oklahoma4 | Pennsylvania | South Carolina |
| South Dakota4 | Vermont3 | Wisconsin | Wyoming |
3 sometimes
4 if the home owner requests it
Mortgage Industry Standards Maintenance Organization (MISMO)
MISMO® is the standards development body for the mortgage industry. MISMO developed a common language for exchanging information for the mortgage finance industry. MISMO standards are accepted and deployed by every type of entity involved in creating mortgages, and they are required by most regulators, housing agencies and the GSEs that participate in the industry.
mortgage insurance
A policy that protects a lender (the mortgagee) if the borrower (the mortgagor) defaults on the mortgage loan. Many government loans and some conventional loans require mortgage insurance if a loan has a loan‑to‑value (LTV) over 80%.
mortgage‑to‑income ratio (or front‑end ratio)
Used with the debt‑to‑income ratio (also called back‑end ratio) to determine how much of a mortgage someone can afford. The front end ratio divides the potential housing expense by the borrower’s gross monthly income. It typically has a maximum limit of 28%.
multifactor authentication (MFA)
A broader security method that requires two or more independent credentials from different categories:
-
Something you know (password, PIN)
-
Something you have (smartphone, hardware token)
-
Something you are (biometric data like fingerprint or facial recognition)
MFA includes two or more factors, while 2FA specifically uses exactly two.
navigation menu
In the Simplifile application, the “navigation menu” is the gray bar in the left panel that is used to navigate Simplifile application pages.
The navigation menu items displayed to a user are determined by the by the organization, active services, roles, and permissions. The items in the navigation menu are not the same for all Simplifile users.
non‑qualified mortgage
A non‑qualified mortgage does not meet the government requirements for a qualified mortgage, but the lender documents show how the buyer’s ability to repay the loan was determined. For more information, see Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB).
prequalification
A preliminary, non‑binding review of a buyer’s financial and credit information that can help a lender advise a borrower about how much of a mortgage he/she can afford. The information provided is not verified. The next step is preapproval.
probate
The legal process of settling an estate after someone’s death, typically handled by lawyers and based on a will. In real estate, probate documents may be recorded to give notice regarding the ownership of property after the owner’s death. A home sold in probate court can be more expensive with more types of fees, and the sale can take more time than a traditional home purchase.
qualified mortgage
A loan with terms and restrictions that make it more likely that a borrower can afford the monthly payments. For more information, see Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB).
qualifying ratios
Tools a lender uses to determine a borrower’s ability to repay a loan.
The mortgage‑to‑income ratio (or front‑end ratio) compares the total housing expense with the borrower’s gross monthly income and typically has a maximum limit of 28%.
The debt‑to‑income ratio (also called back‑end ratio) compares the total housing expense plus any other consumer debt with the borrower’s gross monthly income and typically has a maximum limit of 35%. If one or both of the qualifying ratios is over the maximum, compensating factors such as a high FICO score or a low loan‑to‑value may still allow the borrower to take out the mortgage.
recipient
In Simplifile, a recording county (or jurisdiction or recipient) receives documents for recording. Counties (or jurisdictions or recipients) are integrated into Simplifile in the following primary ways:
- Quick Start jurisdictions log directly into Simplifile and record documents through the Simplifile application. After recording, the documents are maintained in our system but the county can print or save a copy for their records.
- Quick Start Plus jurisdictions log in and record documents through the Simplifile application, but after recording an upload queue in Simplifile lets the county (or jurisdiction) transfer recorded documents to a land records system. Land record systems provide long‑term storage of eRecordings and are typically connected with the county’s website.
- Vendor / 3rd Party jurisdictions maintain a separate software system (such as Property Info, Brown Tech, or Harris Recording) where Simplifile imports data entered by submitters into Simplifile. Each package receives a tracking number (RID) that both Simplifile and the vendor system use to track the package. The vendor system records and maintains the documents.
reconveyance (for release, satisfaction, or sanctification of mortgage)
The official proof, often a deed, which shows that a lien, mortgage, deed of trust, or similar item has been paid off and the related property is free and clear of that specific repayment obligation.
Reconveyance is a term used in some states which use deeds of trust as a mortgage on real property to secure payment of a loan or other debt. Reconveyance means the transfer of title by the trustee back to the borrower when the secured debt is fully paid.
remote ink notary (RIN)
Remote ink notarization is a form of notarization that is statutorily authorized in two states (MT and SD) and was also authorized under emergency orders in a number of states during the coronavirus public health emergency. RIN allows the signer and notary to execute and notarize a paper document while leveraging audio‑visual communication technology for the “appearance” requirement. Specific requirements vary, but essentially the paper document must be transmitted between the parties for wet‑ink signatures. While IPEN and RON produce notarized electronic records, RIN produces notarized paper records.
remote online notarization (RON)
Remote online notarization (RON) is a newer option and is less widely accepted than in‑person electronic notarization (IPEN). RON doesn’t require the signer and notary to be in the same location and can typically be done via webcam. RON requires an identity verification process and secure video communication that is stored for a specified duration. Depending on the state, there may be additional rules. Many states require the RON technology vendor be registered with the secretary of state. RON is a newer option and is less widely accepted than IPEN. RON doesn’t require the signer and notary to be in the same location and can typically be done via webcam. RON requires an identity verification process and secure video communication that is stored for a specified duration. Depending on the state, there may be additional rules. Many states require the RON technology vendor be registered with the secretary of state.
restrictions / restrictive covenants [or conditions, covenants, and restrictions (CC&R)]
Limits in a real estate contract such as a mortgage or a deed that require the owner of a property to follow certain rules and conditions. Such covenants are usually meant to help maintain the value and integrity of the property. Restrictions can be imposed by a builder, developer, neighborhood association, or HOA.
RID
See Remote ID (RID).
sales and purchase agreement (SPA)
See purchase and sales agreement (PSA) [also called sales and purchases agreement (SPA)].
satisfaction of mortgage (or satisfaction)
A deed of reconveyance is a document which transfers title in the property back to the borrower from the trustee and it is used to acknowledge that the borrower has fully paid what he or she owed under a deed of trust. A Satisfaction of Mortgage is used to acknowledge the same of a mortgage agreement.
sheriffs deed
A deed that gives ownership rights in property bought at a sheriff's sale. A sheriff's sale is a sale conducted by a sheriff upon order of a court after a failure to pay a judgment. Often, property that is involved in a mortgage foreclosure is subject to being sold at a sheriff's sale.
subject to mortgage
When a buyer makes the payments on an existing mortgage but is not personally liable to make the payments. If the buyer stops making payment, he or she loses the property and all the money paid. This form of purchase is most often used in a distress sale or as an attempt to save the mortgage holder from foreclosure. Compare to assumption of mortgage.
subordination agreement
An arrangement that gives the interest of one party prevalence over the interest of another. For example, a subordinated mortgage takes a secondary position to some other document, such as a first mortgage. Any subordinated mortgage is paid only after the mortgages with priority are paid.
substitution
When one party to a document is replaced by another party but the document is not modified. Survey. The measurement of a parcel of real estate by a licensed surveyor that shows specific details about the shape, size, location, and physical description of the property, including the location of any improvements.
tag ‑ mini status
![]()
Mini status tags are small status icons attached to other icons for a specific function, in this example, disbursement status for a fee. These mini status tags are used when there is limited space that precludes the use of labels. The combination of two icons allows contextual status in a compact space. Mini status tags are used sparingly.
tag ‑ status
![]()
Status tags can be used for any item needing a strong visual indicator of status. Selecting status a tag may launch a modal with more detail about the status or navigate the user to another page. If you move and hold the cursor over a status tags, a tooltip is displayed describing the result of a select interaction. Status tags do not include icons.
term
In real estate, the length of time it takes to pay a mortgage in full. See also amortization.
third‑party county
A county that uses another vendor's (the third party) software that we have integrated or will integrate with Simplifile is called a third‑party county. In third‑party counties, Simplifile sends the documents to the county and an integration manages the transactions between Simplifile and the vendor's software.
title insurance (also called loan policy, lender's policy, and mortgagee's policy)
A policy usually purchased by the buyer that protects against claims that may arise against a property’s title. The issuer performs a title search in the county records.
The final title policy is a legal and binding policy issued at closing, as opposed to a title certificate or other preliminary title document.
The owner’s insurance protects the buyer as long as the buyer owns the property.
The mortgage insurance is good until the mortgage is paid off, and covers the lender’s interest, not the owner’s.
trust deed
A notice of the release of merchandise to a buyer from a bank, with the bank retaining the ownership title to the released assets. A trust deed (also called transfer document)A legal document that transfers ownership or title to a property from one person or entity to another. Each type of deed (for example, a disclaimer deed, grant deed, warranty deed, fee simple deed, transfer deed, or quitclaim deed) has some legal differences but they all convey property ownership. Sellers and buyers sign the deed during closing. It is then recorded.
two-factor authentication (2FA)
A security process that requires two different forms of identification to verify a user’s identity before granting access to a system, account, or resource. Typically, this involves something the user knows (e.g., password) and something the user has (e.g., a mobile device or security token).
Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) Finance Statement
A legal document that places or releases a lien on personal property such as fixtures, minerals, timber, crops, or consumer goods attached to a piece of real estate. For example, if a bank grants a loan to a manufacturing company using the building and equipment as collateral, the bank would put a mortgage on the building and a UCC lien against the equipment. UCCs are typically maintained in the offices of each state’s Secretary of State.
UCC Financing Statement is an abbreviation for Unified Commercial Code‑1 which is a legal form that a creditor files to give notice that it has or may have an interest in the personal property of a debtor (a person who owes a debt to the creditor as typically specified in the agreement creating the debt.
Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA)
The Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA) is one of the several United States Uniform Acts proposed by the National Conference of Commissioners on Uniform State Laws (NCCUSL). Forty‑seven states, the District of Columbia, and the U.S. Virgin Islands have adopted the UETA. Its purpose is to harmonize state laws concerning retention of paper records (especially checks) and the validity of electronic signatures.
Uniform Real Property Electronic Recording Act (URPERA)
The Uniform Law Commission (ULC), which also created the model Uniform Commercial Code enacted by every state, drafted and approved in 2004 the Uniform Property Electronic Recording Act (URPERA).
For more information, see the State‑by‑State Guide to URPERA Statutes, Commission Reports and Administrative Codes ‑ chart updated 03/19/2015.
U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD)
Created in 1965, this cabinet‑level agency is responsible for enforcing the federal Fair Housing Act and oversees federal programs such as urban renewal, public housing, rehabilitation loans, FHA subsidy programs, and water and sewer grants. Among HUD’s goals: to create quality affordable homes for everyone, strengthen the housing market, and build inclusive and sustainable communities that are discrimination‑free. The Office of Interstate Land Sales Registration, the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) and the Government National Mortgage Association (GNMA) are all under HUD.
view ‑ card view
Card views are a companion to list views (tables) for content. They are effective at surfacing data or content that would be difficult in a table.
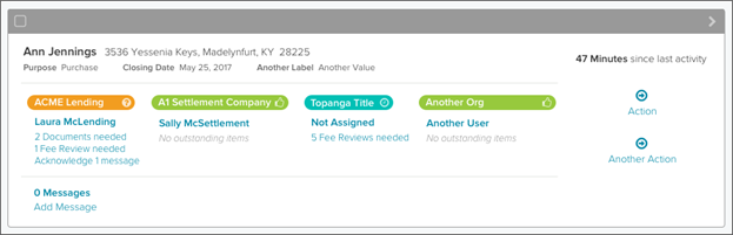
Sorting
If sorting is needed, this functionality can be provided by a dropdown field positioned above the cards.
Navigation
The primary navigation from the card to the data represented by the card (a loan or recording package) is contained in the header of the card.
Actions
If the user is confident in taking a action of the loan or package at this level, the right‑most column has actions they can take.
If more that two actions are likely to be taken from the card view, use a control for the primary action and a "More Actions" control for other actions. More Actions is presented as a dropdown list.
Content
Reference data is useful as context.
Use whatever content is needed for the workflow. This may change from service to service, role to role, or status to status.
Analytics
Card view usage should be analyzed for elements that are not used. If elements are not useful, they should be removed.
window
In the Simplifile application, a “window” is a pop‑up form or message (also known as a "dialog box" or "dialog") that displays over a page which must be completed or closed before you can return to the page. A window often contain fields that can be edited. For example, the Simplifile Add User wizard uses multiple windows. Sometimes a window contains only information like a message. Close a window by completing the action, selecting the window’s Close ![]() button, or selecting outside of the window’s borders.
button, or selecting outside of the window’s borders.
wraparound mortgage / wrap / piggyback mortgage
Typically made when an existing mortgage cannot be paid off. The new loan adds funds to the unpaid first mortgage amount. The new loan is larger, and often has a higher interest rate. Payments are made to the new lender, who makes payments on the original loan.
To b